Learn more about the differences between site and page optimization by applying the pro tips below. Consumer Alert: We’re an affiliate. We hope you love the products/services we recommend! Just so you know, we may collect a share of sales or other compensation from the links on this page. Thank you for using our links and your support, we really appreciate it.
How to Optimize Your Website and Pages for SEO Purposes
Date: 08/10/2022

Introduction
Your website is the first thing potential customers would see when they search for your business. If you want them to be impressed with what they find, you have to make sure your website is optimized for both desktop and mobile devices. It’s not enough just to have a good-looking site; the content has to be easy to navigate and attractive too. Here are some tips on how to optimize your website so that it works well for both desktop users and people browsing with mobile devices as well as search engines:
Keywords
In order to make sure your website is optimized for search engines, you must use keywords in a variety of places:
Use keywords in the title tag. The title tag is the first thing that Google and other search engines see when they crawl your site. It should be descriptive and contain relevant keywords or phrases that users would type into a search engine to find your content. You should also ensure it’s at least 70 characters long as Google will truncate titles longer than this if they are not deemed relevant enough for users to click on them.
Use keywords in headings throughout content pages — but don’t overdo it! Headings help users scan through content quickly, so using them appropriately can help visitors find what they’re looking for faster without having to read everything word-for-word (which isn’t very good UX). However, too many headings can create unnecessary levels of hierarchy within posts which can confuse readers on where they should focus their attention while going through them; try not to go overboard with headings by making sure there aren’t more than three per article/page unless absolutely necessary!
Use alt tags on images containing text descriptions; these are useful because when people share links online, oftentimes they only include images instead of entire webpages – so alt tags provide context about what an image actually contains if someone shares just an image link by itself.
There is also another in-depth article about how to use keywords for optimization on our site, you can view it here.

About Title Tags
When you think about optimizing your website for search engines, you may be tempted to focus on keywords and tags. And while those are important, it’s also important to remember that people use web browsers to look for content on the internet. Your title tag is what appears in their browser tabs and will either entice them to click through or drive them away.
For example:
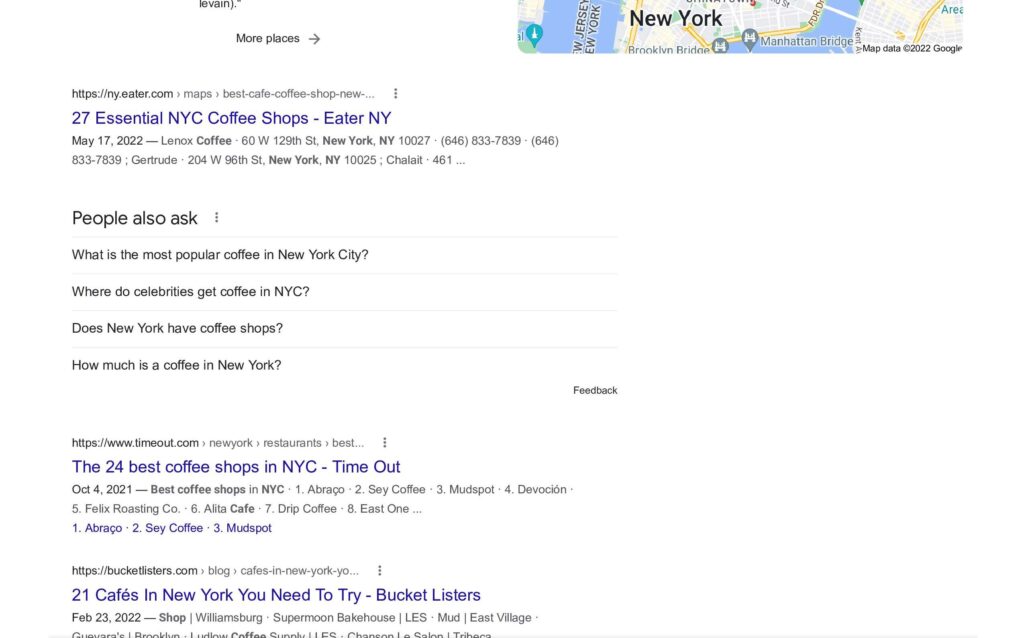
If I search “best coffee shop in New York City” on Google, this is what I see:
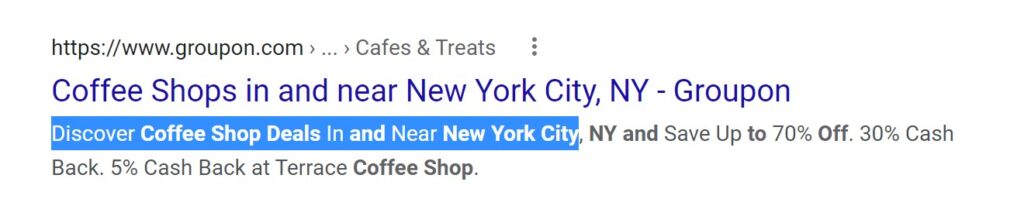
As you can see in Figure 1, there are multiple results with very similar titles and meta descriptions but only one result has a clear call-to-action in its listing that tells me exactly what they want me to do when I arrive at their website (i.e., “Discover Coffee Shop Deals In and Near New York City”). They could’ve put this information in the title tag as it works the same.
Figure 1
Google Search Results for "best coffee shop in New York City"
Header Tags
Header tags are used to add metadata to a page. There are three main header tags: H1, H2, and H3. The difference between these is that they each represent different levels of importance on the page. If you want to make sure people see your most important content first (and not buried in a bunch of other stuff), use an H1 tag at the top of your webpage title text. The search engine also catches this and determines what the page is about, and you don’t want to confuse it!
H2 tags can be used anywhere on the page where you want another heading level without using an H1 tag again. For example, if you have some subheadings under your primary heading that aren’t as important as your main title but still need to be highlighted in some way above regular text paragraphs, use an H2 tag for them instead of just ordinary paragraph text in HTML code.
An H3 tag should always be used after two or more headings with exactly equal importance; otherwise, it’s unnecessary. Learn more about how headers work by watching the video below.
Advanced Header Tags SEO by Missoula SEO Geek
Images and Alt Tags
Alt text is the text that appears when you hover over an image. You can view it in your browser by pressing and holding a mouse cursor over any image on a web page. It’s also visible in Google Images and Pinterest, which means that anyone using these services will be seeing your alt text. Alt Tags help search engines understand what each image is about and where it should be grouped within their indexes. This helps people find you when they search for products or services like yours because it increases the chances of your site appearing higher up in results pages than others without useful alt tags.
How Do I Create Alt Text?
The easiest way to create alt text is to use Canva, which has templates that include appropriate keywords so all you really have to do is add them into each template (you may need some tweaking depending on how many words are used). If you want more control over the design, however, there are plenty of free tools available online such as Textify or My Image Editor from Pixabay (both require registration but don’t cost anything really). You can also make your own templates using Photoshop or Illustrator if those are more comfortable for you!
Pro tip: If you’re using WordPress, you can use a free SEO plug-in called RankMath, which allows you to create alt texts for your images when uploading them, making it so much easier for search engines to understand what your content is about and get users to your site faster.

Links and Image Placement
When it comes to links, the text is the name of the game. Links are usually words that are linked to another website or resource and have the potential to redirect users from one page to another. Let’s say you’re writing about how to make a good sandwich and you want your readers/customers/potential employees to know about some good places nearby that sell deli meat, bread, and condiments. You could link their names or URLs in your content with text like “more info on local sandwich suppliers” or something similar.
Anytime you include links within your content—whether it’s an image file or just plain text—make sure they’re relevant and not just there for decoration. If you don’t have any images at all on your page (or if they’re completely unrelated), then no problem; but if there’s even one image in play, then make sure all relevant information has been included in its file name so as not to confuse anyone who sees it!
Page optimization is a good start, but the best thing you can do for your business is to optimize your whole website.
The two most common mistakes made by small businesses are not optimizing their sites at all or only optimizing certain pages of their site. This means they’re missing out on opportunities to improve engagement and conversions. Every page, every file, every image, and anywhere relevant to the website, must be optimized and mobile-friendly (you don’t want to gamble on potential traffic, You. Will. Lose.)
Speed Issues
Speed is a key part of the user experience. The faster your website loads, the better it is for your users. You want to make sure that your website or page loading time is fast enough to provide a good user experience. Here are some tips:
Make sure you have plenty of bandwidth available so that pages can be loaded quickly and smoothly all of the time (at least 25 Mbps). You can test your internet speed here. You need to make sure your internet speed is irrelevant to your website/page load time (this way you’ll know how deep you need to go to optimize your site speed).
Test your page speed by typing your URL or target page here. If your page speed score is low, proceed to optimize your page and ultimately your site.
Remove unnecessary plugins/widgets from WordPress sites, since these can slow down site performance significantly! If possible move hosting if needed because shared hosting packages do not always offer enough resources when running multiple sites which could cause problems for one another later down the line if not properly managed correctly; also keep in mind that shared servers usually don’t come equipped with unlimited bandwidth unlike dedicated servers do, so as soon as gigabytes reach max capacity then traffic speeds decrease dramatically throughout the entire network, so do yourself a favor before signing up here instead go elsewhere where they offer unlimited resources 🙂
Mobile-Friendly Design
Mobile-friendly design is important for SEO. If your site looks weird on mobile devices (i.e. web browsers on smartphones) then users tend to lose engagement and bounce. You will lose potential sales, even if they choose to call your number and get on a phone call after visiting your site.
Mobile-friendly design is important for customer experience. A professional layout that shows on a user’s mobile web browser, can make a great first impression, encouraging the user to revisit, even if they don’t contact you the first time. Remember how we mentioned your site is most likely the first thing a customer sees at the beginning of this article? This also includes the way your site shows up on mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, etc.)
Mobile-friendly design is important for bounce rate. You want to make your site as engaging as possible so that the user stays and learns more about your products and services. The design, layout, and content have to be easy to read and understand; remember some users may visit your site on a bus, or a train or even wait their turn at the dentist’s office. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly!

Few Clicks to the Sale
Lastly, a good website should be easy to navigate, with clear paths for visitors to take. You want your site visitors to see what you want them to see and quickly get there.
That’s why it’s important for your navigation menu on the homepage of your website or page to be clear and concise. Think about how many people click on “Contact Us” when they visit a restaurant website — not many! Instead, they look at the menu and try their best guess as to where each item is located on a Menu page (if they even have one).
Closing Statement
Optimizing your page for search engines is just the beginning. The most important thing you can do for your business is to optimize your entire website so that customers find what they need more easily and are more likely to make a purchase or contact you for your services. At Lieutenant Marketing, we build websites not only optimized for search engines but optimized for user experience (UX). Hence, we passionately help you with your digital marketing needs to generate more traffic for your business. Contact us today for a custom quote and we’ll get your traffic started!







